Revision Control
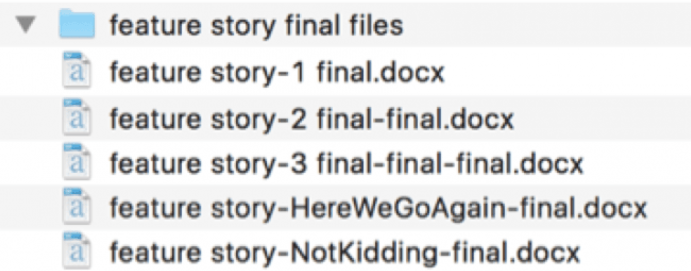
What happens in software development?
- 👩🏻💻 Write a program
- 👩🏻💻 Work on it a bit more
- 🎉 It's ready for use
- 😊 You use it
- 💡 You think of a new feature
- 😎 You add the feature
- ⚠️ Eek a bug
- 🆒 Fix the bug
- 😊 Use the program some more
- ⚡️ Start work on big new feature
- 🚨 Eek! Another bug!
- 😕 Now what?
- 🍝 Big feature not finished yet. Code threads are everywhere like spaghetti. You can't add a new feature because nothing is working right now.
- 🤯 Oh dear
Why do we need git?
When there are multiple developers, someone might ask:
- what was done?
- why was it done?
- who did it?
- when did they do it?
- how can we undo it?
Helpfully git…
- tracks every code change
- records commit messages
- keeps an audit trail
- facilitates collaboration
- enables rollback
Git Glossary
- Repository (Repo):
- A folder where Git tracks your project.
- Working Tree:
- All the files and folders that Git is tracking, plus any new files you add.
- Branch:
- An independent line of development within your project.
- Stage:
- Tell Git which changes you want to include in the next snapshot.
- Commit:
- Make a snapshot of your project at a specific point in time.
- Clone:
- A copy of a repository from a remote server to your local machine.
- Push:
- Uploading your local commits to a remote repository.
- Pull:
- Downloading changes from a remote repository to your local machine.
Core git commands
git init: Create a new Git repository in the current directory.git status: Show the status of changes in the working tree.git add <file>: Stage changes to a specific file for the next commit.git commit -m "message": Create a new commit with a descriptive message.git push: Upload local commits to a remote repository.